TLDR; SEE CLINICAL INFO 1 PAGER HERE
Last updated: 6/12/20
List of Clinical Information Sources
Feedback form: https://forms.gle/KTy5nLFmLL5DwXubA
Basic Information
- Pathogen: SARS-CoV-2
-
Disease: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- (+) ssRNA, large, enveloped beta-coronavirus
- Zoonotic origin with mammalian sources including the bat, pangolin, or snake
- SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein binds the ACE2 receptor and requires TMPRSS2 and furin proteases to facilitate host cell entry
- viral particle entry via respiratory droplets
Pathogenesis
TLDR; SEE PATHOPHYSIOLOGY 1 PAGER HERE
Great resource: https://www.cell.com/immunity/fulltext/S1074-7613(20)30183-7
Overview
- Infection of type II pneumocytes in the lung by SARS-CoV-2 particles
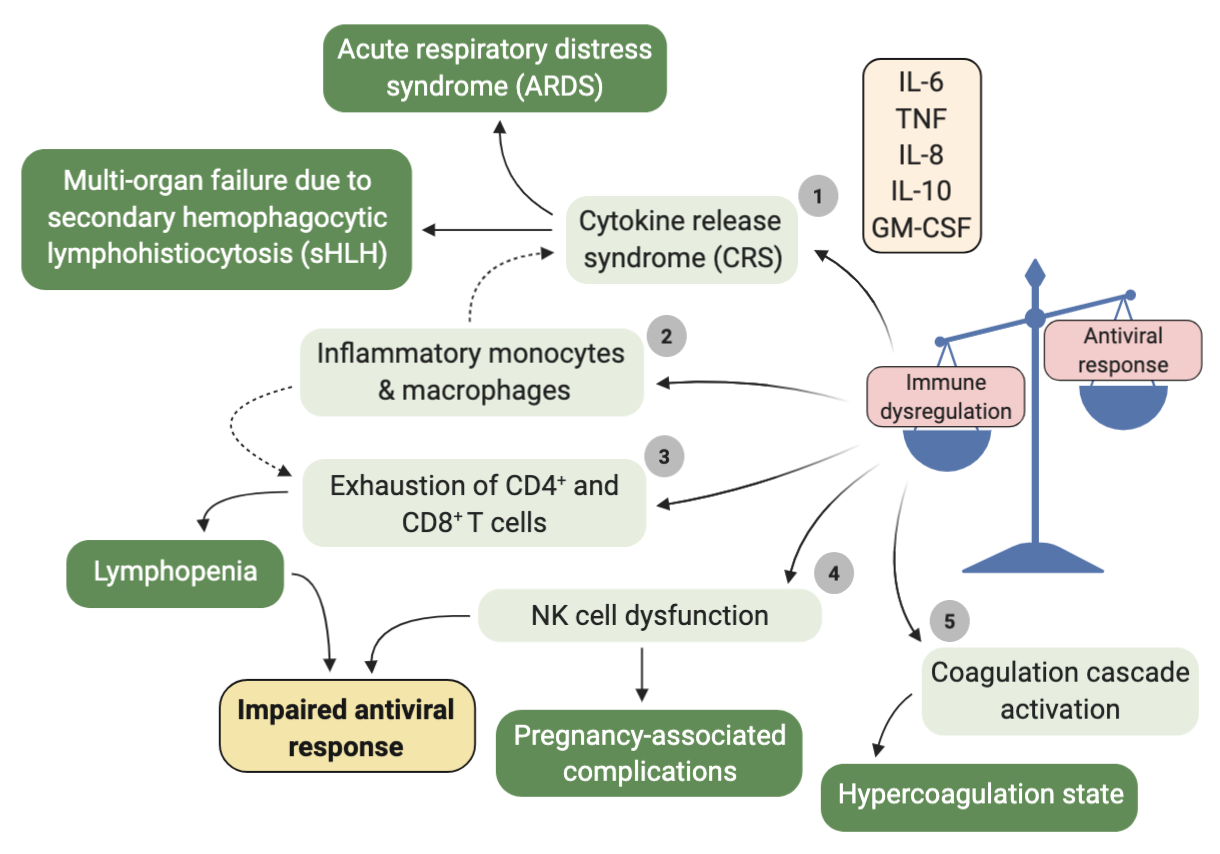
- Impaired interferon response and cytolysis results in increased levels of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in the circulation (IL-6, IL-8, TNF)
- Vasodilation and increased vascular permeability
- Edema and compression of alveoli
- Decreased production of lung surfactant, reduced gas exchange → Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
ACE-2 Receptor See graphic here
-
SARS-CoV-2 enters cells through the ACE2 receptor
- Negative regulator of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)
- Promotes vasodilation via conversion of ATII to angiotensin 1-7
- Ubiquitously expressed by multiple organ tissues, with local regulatory function
- Lung
- Heart and vasculature
- Kidney
- Intestines
- Liver
- Brain
- Heart and vasculature
- ACE2 is also described to modulate β-cell activity in the pancreas.
- SARS-CoV-2 binds the ACE2 receptor, disabling the ACE2 signaling axis may explain
- potential gendered differences in the mortality and susceptibility of male and female cases.
- range of COVID-19 symptoms at onset, including headache, diarrhea, hepatic dysfunction, stroke, and hypertension.
- major COVID-19-associated complications, where ACE2 is vital in its niches, including cardiac injury, gastrointestinal symptoms, endocrinopathy, and meningitis.
Immune Dysregulation in COVID-19
See Graphic on Hypercoagulation HERE
Great resource: https://www.cell.com/immunity/fulltext/S1074-7613(20)30183-7
Epidemiology
- R0 (no. of infections from 1 case) = 2.5-2.9
- Attack rate = 0.25%
- CFR (case fatality rate) = 1.3% (influenza CFR = 0.1%)
- Incubation time = 5.2 days (to 14 days)
Affected populations
- Pediatric patients (multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children [MIS-C]):
- Kawasaki-like syndrome with fever, hypotension, GI symptoms, rash, myocarditis; respiratory symptoms may be absent
- Pregnant women
- complications of the maternal/placental vasculature (e.g., microthrombi formation), preeclampsia
- Elderly patients
- mortality in pts > 75 is 75x rate among 18-44-year-olds
Prevention
Control Strategies (WHO)
- Social distancing / quarantine
- Use of face masks
- Contact tracing and screening
Recommended Precautions
- Hand hygiene
- soap/water for 20 sec when visibly soiled, before eating, and after restroom use
- otherwise, alcohol-based hand rub and gloves
- Airborne precautions for aerosolizing procedures (intubation, suction, NIPPV)
- Droplet precautions (all else)
Symptoms
- Cough (76%), fever (98%), dyspnea (50%), myalgias or fatigue (44%), GI (10%)
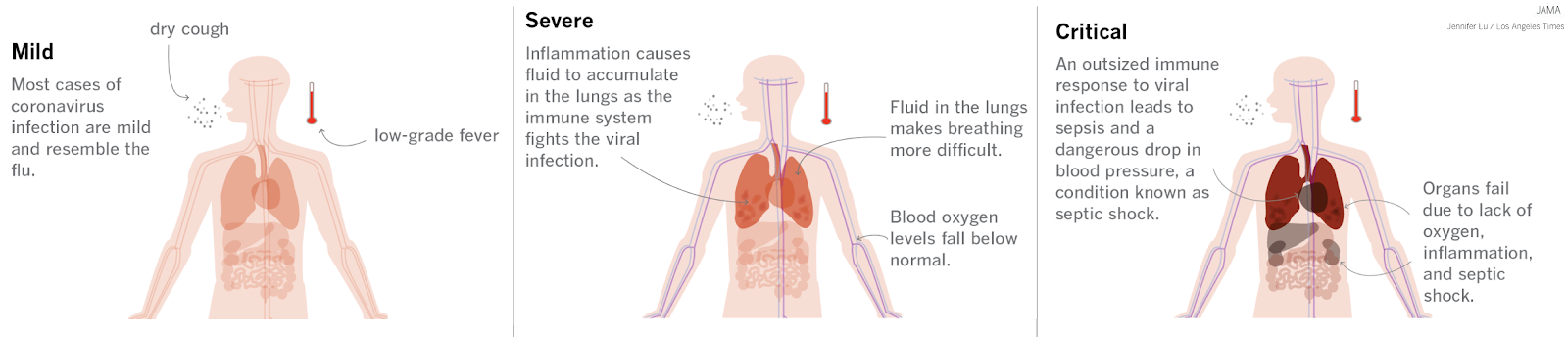
- Presentation rates:
- asymptomatic (1.2%)
- mild to medium (80.9%)
- severe (13.8%)
- critical (4.7%) -- death (2.3%)
Laboratory Assessment
Inflammatory Markers
- ↑ CRP, ferritin, D-dimer, PCT, LDH
- ↑ IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α
Liver Function Tests (LFTS)
- ↑ AST/ALT
- ↑ Total bilirubin
Basic metabolic panel (BMP)
- ↑ BUN / Cr
Complete blood count (CBC)
- ↓ lympho-/leukocytes
- ↑ neutrophil count & neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio
Imaging
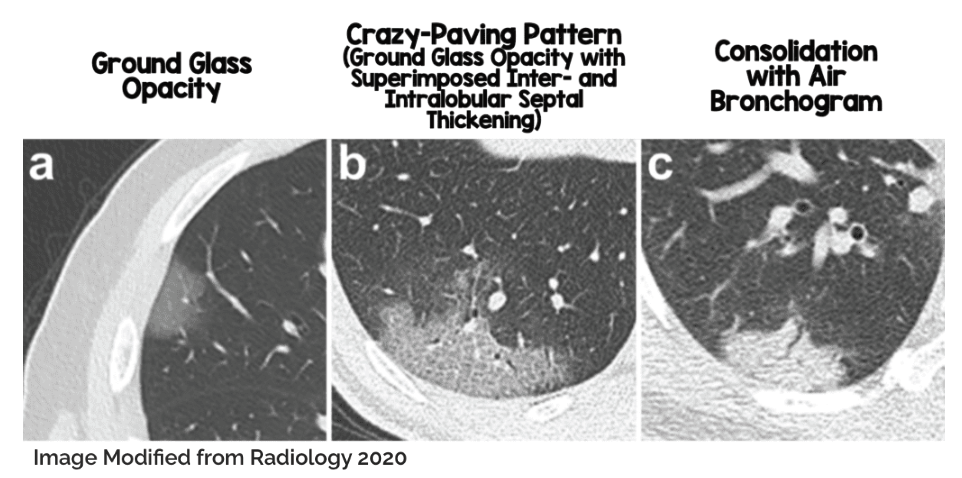
CXR/CT
- Bilateral, multilobar involvement
- Ground glass opacities and consolidation
- CT should only be used when impacting management → CT is sensitive, but not specific
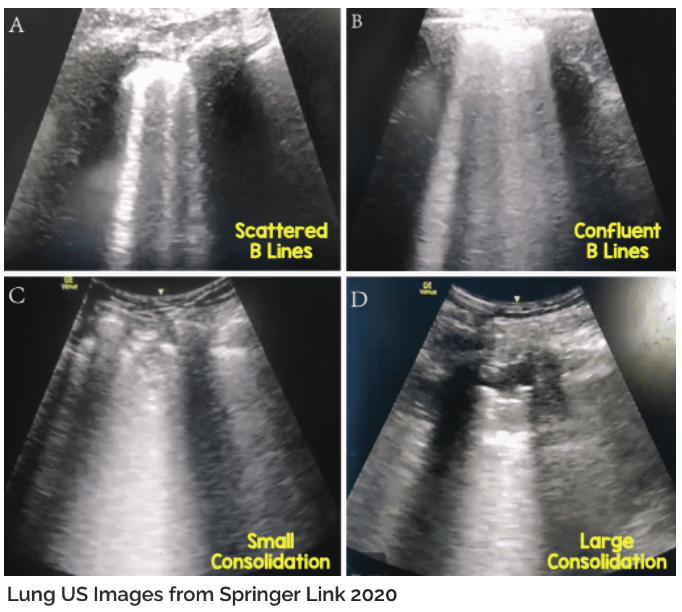
POCUS (Point-of-care ultrasound)
- B-lines, pleural lines, air bronchograms
Prognosis
Risk factors
- Age
- Cardiovascular, endocrine, liver and pulmonary disease
- CKD
- Obesity
- Cancer
- Residence in nursing homes/long-term care facilities
Independent Predictors of Clinical Severity
Great resource: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.05.28.20115758v1
- ↑ CRP, LDH, lymphocyte count, IL-6, TNF-α, D-dimer
- ↑ Neutrophil: lymphocyte ratio
Complications
- ARDS
- Sepsis
- AKI
- Transaminitis
- Venous thromboembolic events
- Cardiac (cardiomyopathy, HF, MI, arrhythmias)
- Empyema
COVID-19 calculators
-
https://www.mdcalc.com/covid-19 includes calculators that:
- Predict risk of critical illness in hospitalized patients
- Need for intubation
- Likelihood of coagulopathy
Management Strategy
Testing
- RT-PCR (order early - can take days; see testing criteria)
- 66-80% sensitive; i.e. 20-34% false negative rate
Basic care
- Lung protective ventilation, proning, restrictive fluid management and management of organ failures
- SpO2 target ≥ 93%
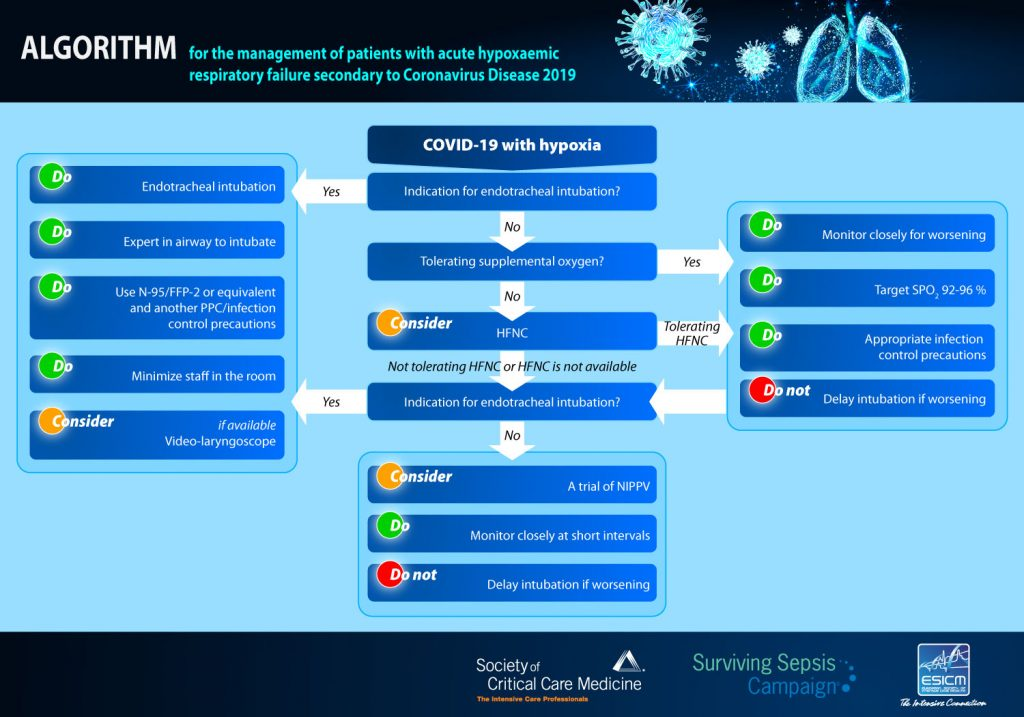
- Oxygenation – HFNC, face mask, or non-invasive ventilation
- Systemic anticoagulation (see pathway INSERT LINK TO ANTICOAG PAGE HERE)
Mechanical ventilation
- Indicated by SaO2 < 93-96% + acute lung injury
- 7 P’s: PEEP, Paralysis, Prone positioning, Prostacyclins, Pleural evacuation, Peeing (diuresis), Peripheral oxygenation (ECMO)
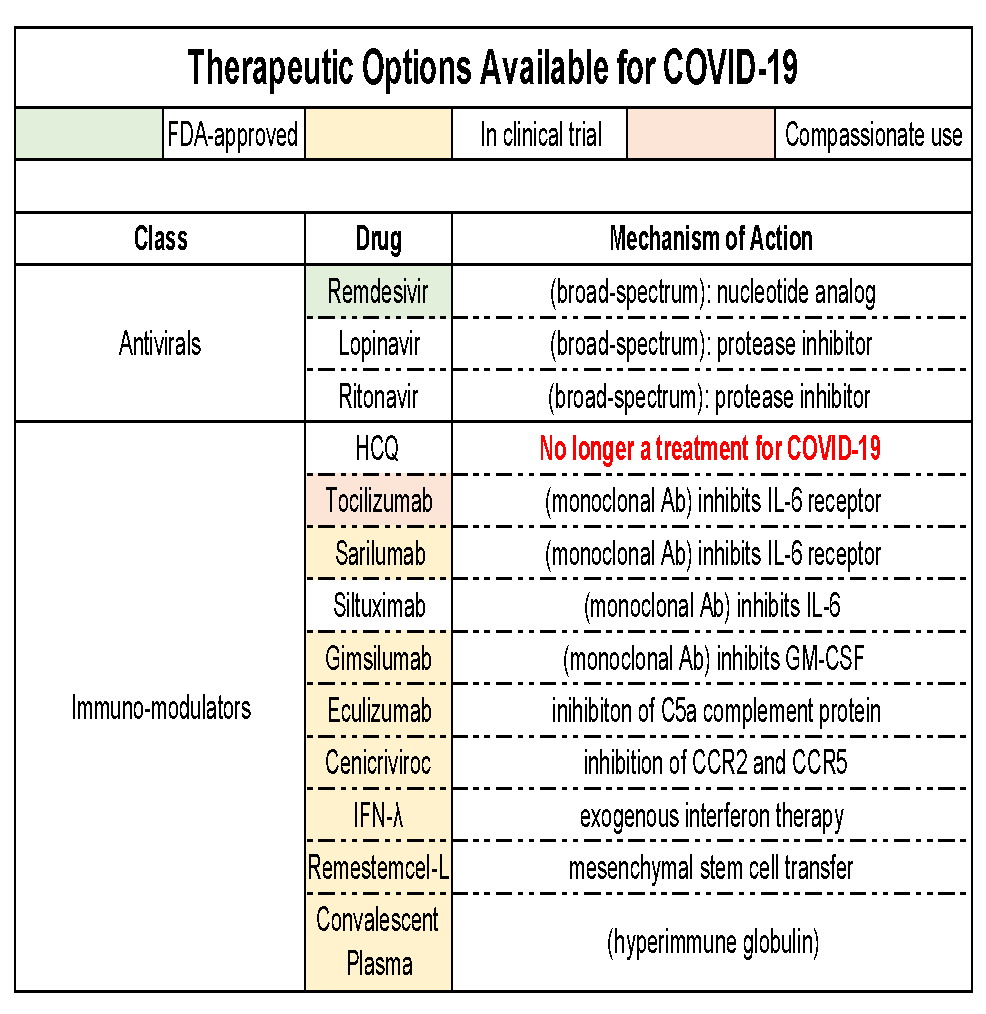
Drugs / vaccines
- Remdesivir is the only FDA-approved drug (nucleotide analog, inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase)