MSHS Treatment Guidelines COVID-19 to look for most updated PDF under “MSHS Treatment Guidelines for COVID-19 Adults - COVID-19 Anticoagulation Algorithm” updated 4/28/20. Refer to this document for specific dosages
General Anticoagulation Pathway
All admitted patients with COVID-19:
-
Assess for VTE risk factors, signs or symptoms of DVT and PE, severity, and bleeding risk.
- Assessment of severity is based on clinical judgment, and includes:
- symptoms (worsening dyspnea)
- signs (e.g., RR >24)
- oxygen requirement (e.g., ≥6L O2 NC)
- biomarkers (e.g., D-dimer >1.5 or increasing)
- Increased risk for bleeding includes:
- active bleeding
- PLT <50K
- INR >1.8.
- Assessment of severity is based on clinical judgment, and includes:
Who should adhere to the Anticoagulation Pathway?
- All admitted patients with moderate to severe COVID-19
- Exclude patients with high risk of bleeding
What labs should be tracked daily?
- Daily CBC
- PT/PTT
- D-Dimer
Rationale for early anticoagulation and type of anticoagulant?
- Early anticoagulation prevents propagation of microthrombi and is associated with decreased mortality.
- Choice of anticoagulation: Heparins bind tightly to COVID-19 spike proteins and downregulate IL-6 and directly dampen immune activation. DOACs do NOT have anti-inflammatory effects like Heparins
Appropriate steps based on risk level of coagulopathy
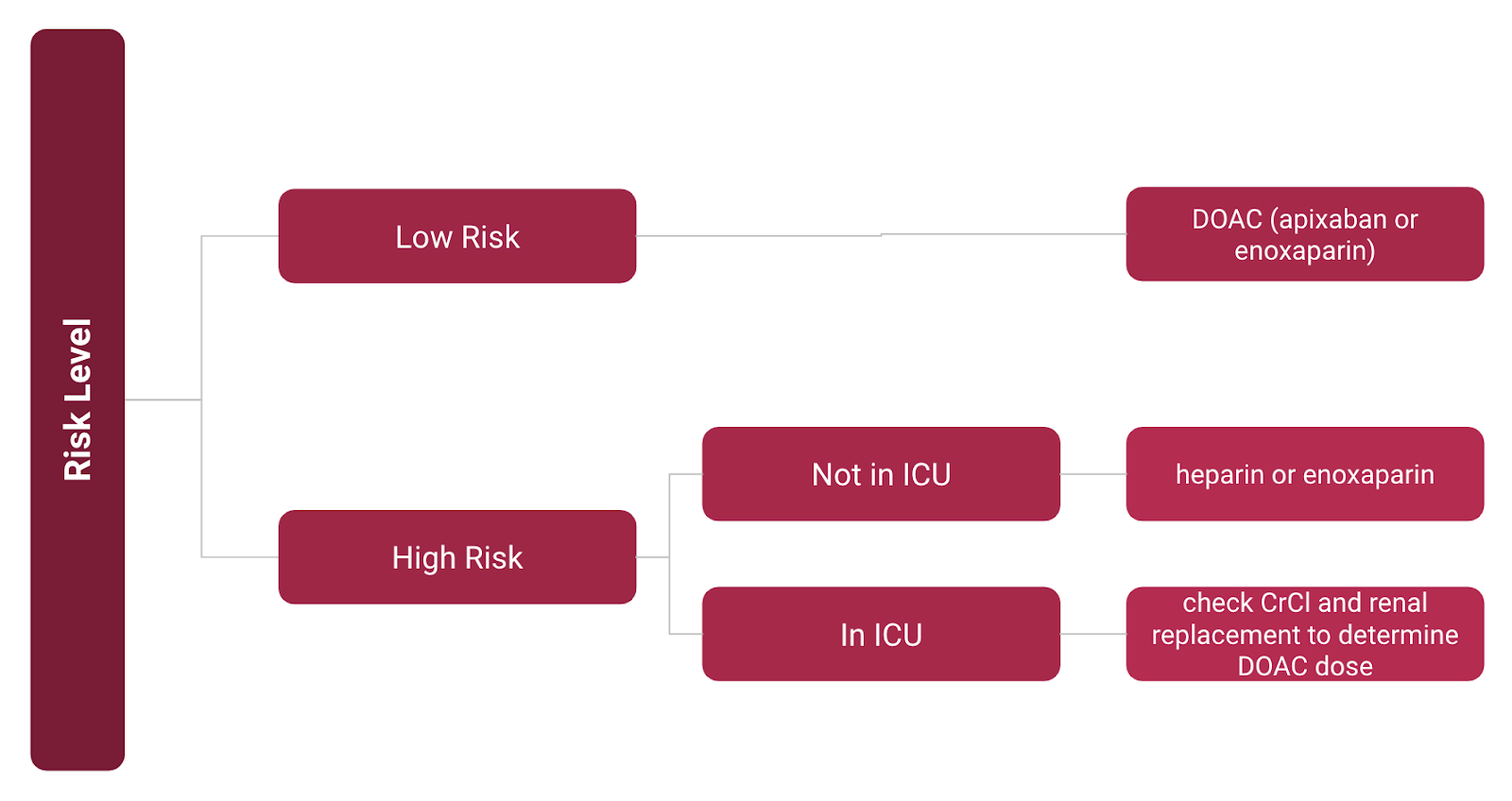
What determines High Risk?
- Worsening dyspnea
- RR > 24
- O2 > 6L O2 NC
- D-dimers > 1.5
- High creatinine
- Increased CRP
When to discontinue anticoagulation
- Hold anticoagulation if evidence of bleeding, platelet count <50K, INR >1.5
- Upon discharge, consider 2 weeks of prophylactic anticoagulation if patient on anticoagulant in hospital